Glucagon CAS 16941-32-5 Promotes glycogenolysis and glucose production to raise blood sugar
Product Name: Glucagon
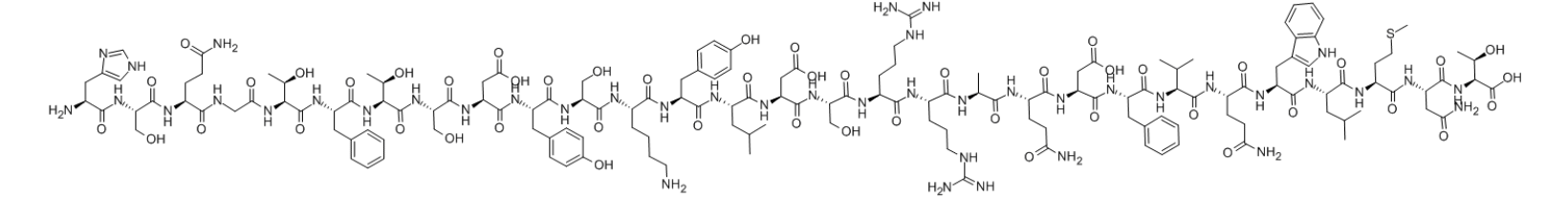
Synonyms: GLUCAGON 1-37;GLUCAGON (1-37) (PORCINE);GLUCAGON 37;GLUCAGON ACETATE;HSQGTFTSDYSKYLDSRRAQDFVQWLMNTKRNKNNIA;H-HIS-SER-GLN-GLY-THR-PHE-THR-SER-ASP-TYR-SER-LYS-TYR-LEU-ASP-SER-ARG-ARG-ALA-GLN-ASP-PHE-VAL-GLN-TRP-LEU-MET-ASN-THR-LYS-ARG-ASN-LYS-ASN-ASN-ILE-ALA-OH;Glucagon 1-29;Glucagon(1-29) Human HCl
CAS: 16941-32-5
MF: C153H225N43O49S
MW: 3482.75
EINECS: 685-611-6
Product Categories: Amino Acid Derivatives;Peptide;GlucagonIslet Stem Cell Biology;Islet Stem Cell Differentiation;Hormones;Other Protein/Peptide Hormones;Glucagon and Glucagon-Like PeptidesPeptides for Cell Biology;GlucagonsIslet Stem Cell Biology;Cytokines Growth Factors and Hormones (Obesity);Gastrointestinal Peptides;GlucagonObesity Research;API;Diabetes Research
Mol File: 16941-32-5.mol
Glucagon, also known as glucagon, is a straight-chain polypeptide hormone secreted by pancreatic islet α cells, containing 29 amino acids, with molecular formula and relative molecular mass of C153H225N43O49S = 3482.8. China has synthesize this hormone. It is a kind of white, odorless, and tasteless fine crystalline powder at room temperature. Glucagon is nearly insoluble in water and most organic solvents, while it is soluble in dilute acid and dilute alkali solution. Most of the preparation are hydrochloride which is dissolved in water. It is known that glucagon must retain its molecular integrity in order to exert its physiological activity. The glucagon structure of human and mammalian (rabbit, bovine, porcine, rat, etc.) may be consistent, while slightly different birds.
Glucagon is a polypeptide consisting of 29 amino acids and is secreted by the alpha cells of the islets of the pancreas. Glucagon is produced from the pro-glucagon gene, initially as the precursor pro-glucagon, which is processed tissue-specific in pancreatic alpha cells to form glucagon and in intestinal cells to form GLP-1 and GLP-2.
It is generally accepted that insulin and glucagon are the main hormones involved in the pathophysiology of diabetes, but the role of glucagon in diabetes is complex and controversial in some cases. The role of glucagon in currently used hypoglycemic agents is receiving increasing attention, and the continued development of glucagon targeted therapy highlights the important contribution of glucagon in optimizing diabetes management.
Glucagon is a counter-regulatory hormone that stimulates hepatic glucose production to avoid hypoglycemia. Glucagon receptors are located on hepatocytes, and glucagon binding sites have also been identified in the kidney, heart, gastrointestinal tract, adipose tissue, brain and spleen. Based on studies in dogs, approximately 17% of glucagon is degraded by the kidneys and 20% to 25% is degraded in the liver. The release of glucagon in response to hypoglycemia has been well established and is mediated through autonomic, endocrine and paracrine mechanisms and possibly also through direct sensing of blood glucose levels by alpha cells. The exact molecular mechanisms by which cells secrete glucagon are not fully understood, but involve potassium adenosine triphosphate (KATP) channels and calcium channels.
In normal physiology, glucagon secretion during hyperglycemia is inhibited by the cellular secretion products insulin, zinc and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which are released in response to meals and elevated blood glucose. When blood glucose levels fall, beta cells reduce the production of these products, thereby eliminating their inhibitory effect on alpha cells. This mechanism, known as the “shutdown” hypothesis, ultimately leads to an increase in glucagon secretion when blood glucose is too low. Growth inhibitory hormone, which is produced by δ cells and GLP-1 in the islets, also inhibits glucagon secretion.
In both type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), plasma glucagon levels are too high. Glucagon, a regulatory hormone that promotes hepatic glucose production, prevents hypoglycemia under normal physiological conditions. In patients with diabetes, glucagon secretion may be uncontrolled, which leads to problems with glucose homeostasis. Some treatments for diabetes are effective by inhibiting the secretion or action of glucagon, as well as glucagon-specific targeted therapy.
Glucagon CAS 16941-32-5 Chemical Properties
density 1.53±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
storage temp. Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C
solubility Practically insoluble in water and in most organic solvents. It is soluble in dilute mineral acids and in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
form powder
Function and Application of Glucagon CAS 16941-32-5
1、Raise blood glucose effect: It can activate liver phosphorylase, promote hepatic glycogen decomposition and glycogen isogenesis, and raise blood glucose.
2、Positive inotropic effect: It can increase intracellular cAMP content, enhance myocardial contractility, increase cardiac output and work per beat. Its positive inotropic effect can still be exerted after applying sufficient amount of cardiac glycoside, and it is not blocked by propranolol. Although it can increase heart rate and blood pressure, it does not cause arrhythmia. The mechanisms are: (1) activating adenylate cyclase to convert adenosine triphosphate into cyclized adenosine monophosphate, which increases myocardial contractility; (2) promoting hepatic glycogenolysis and increasing blood glucose level; (3) promoting insulin release Chemicalbook release, improving myocardial utilization of glucose and promoting myocardial anaerobic enzymes, thus improving myocardial energy metabolism. Combined with digitalis-like cardiac glycosides, it can increase the efficacy.
3. Effects on kidney: dilate renal blood vessels, improve renal blood flow, and promote excretion of sodium, potassium and calcium.
4. Effects on digestive system: can cause relaxation of smooth muscles of stomach and duodenum, small intestine and colon, inhibit peristalsis of stomach, small intestine and colon, and increase secretion of bile and intestinal fluid.
5. Effects on secretory system: excite adrenal medulla, promote The release of catecholamines. It can also promote the secretion of insulin, thyroid hormone, calcitonin and growth hormone.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.